Information Technology
Information Technology, often abbreviated as IT, is a broad field that encompasses the use of computers, software, networks, and electronic systems to store, process, transmit, and manage data and information. IT is fundamental to modern society, powering everything from personal computing devices and the internet to business operations, communication, and technological innovations. It plays a crucial role in improving efficiency, productivity, and communication across various industries and sectors.
Six Types of Information Technology:-
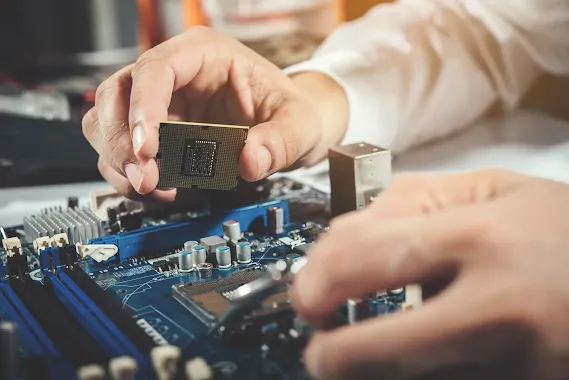
1. Hardware Technology:
Hardware technology refers to the physical components of computing devices. This category includes various types of devices such as personal computers, servers, smartphones, tablets, and networking equipment. Hardware technology has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in processing power, storage capacity, and connectivity. Moore's Law, which predicts the doubling of transistors on integrated circuits approximately every two years, has been a driving force behind the rapid development of hardware technology.
Additionally, innovations like solid-state drives (SSDs), graphics processing units (GPUs), and quantum computing have further expanded the capabilities of hardware technology. The integration of sensors, cameras, and other components into everyday objects has given rise to the Internet of Things (IoT), a subfield of hardware technology that connects physical devices to the internet for data collection and automation.
2. Software Technology :
Software technology refers to the programs and applications that run on hardware devices. This includes operating systems, productivity software, games, and specialized applications for various industries. Software development has become a critical aspect of IT, with programming languages like Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript serving as the building blocks for creating software solutions.
The software industry has also seen the emergence of open-source software, which is developed and distributed freely, fostering collaboration and innovation within the developer community. Cloud computing platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide infrastructure and tools for deploying and managing software applications globally, enabling scalability and flexibility.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are subsets of software technology that have gained immense traction. These technologies use algorithms and data to enable machines to learn and make decisions, leading to applications like natural language processing, computer vision, and autonomous systems.
3. Networking Technology :
Networking technology encompasses the infrastructure and protocols that allow data to be transmitted between devices and across the internet. It includes wired and wireless networks, routers, switches, and communication protocols like TCP/IP. The development of high-speed internet, from dial-up connections to fiber-optic networks, has revolutionized the way information is shared globally.
The advent of 5G technology promises even faster and more reliable wireless connections, enabling advancements in IoT, autonomous vehicles, and remote work. Additionally, virtual private networks (VPNs) and encryption technologies play a crucial role in securing data during transmission, ensuring privacy and data integrity.
Networking technology also includes the concept of cloud computing, where data and applications are hosted on remote servers accessible via the internet. This model has transformed how businesses and individuals access and store information, reducing the need for on-premises infrastructure.
4 Database Technology:
Database technology involves the storage, retrieval, and management of structured and unstructured data. Databases are essential for organizations to store and organize vast amounts of information efficiently. Traditional relational databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, use tables and schemas to structure data.
However, the rise of NoSQL databases, like MongoDB and Cassandra, has provided alternatives for handling unstructured and semi-structured data, such as social media posts, sensor data, and multimedia content. These databases are particularly suited for applications with high scalability and flexibility requirements.
Data warehousing is another facet of database technology, focusing on the consolidation and analysis of data from various sources to support business intelligence and decision-making. Big data technologies, like Hadoop and Spark, enable the processing and analysis of massive datasets, opening new possibilities in fields such as data science and predictive analytics.
5. Security Technology:
Security technology is crucial in safeguarding information from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. It encompasses a wide range of tools and practices, including firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication. With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, cybersecurity has become a top priority for organizations and individuals.
Endpoint security solutions protect individual devices, such as computers and smartphones, from malware and phishing attacks. Network security focuses on securing the entire network infrastructure, while cloud security addresses the unique challenges associated with cloud-based services and data storage.
The field of cybersecurity is in constant evolution, with security professionals continuously developing new strategies and technologies to stay ahead of cybercriminals. Threat intelligence, ethical hacking, and security awareness training are vital components of a robust security posture.
6. Emerging Technologies :
Emerging technologies represent the cutting edge of IT innovation. These technologies have the potential to reshape industries and society as a whole. Some notable examples include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI technologies, including machine learning and deep learning, are becoming increasingly integrated into various applications, from autonomous vehicles to virtual assistants.
- Blockchain: Originally developed for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain technology is now being explored for secure and transparent record-keeping in various industries, including finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems at speeds unimaginable with classical computers, impacting fields such as cryptography and drug discovery.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are transforming how we interact with the digital world, with applications in gaming, education, and training.
- Biotechnology: Advances in biotechnology, including gene editing and synthetic biology, have the potential to revolutionize healthcare, agriculture, and environmental conservation.
- 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks and ongoing research into 6G promise faster and more reliable wireless communication, enabling innovations like autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
In conclusion, information technology is a dynamic and multifaceted field encompassing hardware, software, networking, databases, security, and emerging technologies. These categories work in tandem to drive innovation, reshape industries, and improve our daily lives. As technology continues to advance, it is essential for individuals and organizations to stay informed and adapt to the evolving IT landscape.
Tags:
Information Technology


.webp)
.jpg)


